1. Main points
Median household disposable income in the UK was estimated as £25,700 in the financial year ending 2015 (2014/15). This is £1,500 higher than its recent low in 2012/13, after accounting for inflation and household composition, and is at a similar level to its pre-downturn value (£25,400).
The recent increase in disposable incomes has been driven largely by increased household income from employment, due to both average earnings growing in real terms in 2014/15 and continued growth in employment rates.
The median disposable income of the richest fifth of households fell the most following the economic downturn (7.9% between 2007/08 and 2012/13). Since then it has increased, but in 2014/15 remained £2,000 (3.2%) below its previous peak after accounting for inflation and household composition. The poorest fifth of households were the only group whose average income did not fall between 2007/08 and 2012/13 and in 2014/15 the average income of this group was £700 (5.8%) above its 2007/08 value.
Estimates of income inequality for 2014/15 are broadly unchanged from those for the previous financial year (any differences are not statistically significant). Since 2007/08, there has been a slight decrease in overall income inequality on a range of measures, although from a longer-term perspective, income inequality remains above levels seen in the early 1980s.
Income inequality for retired households has increased slightly in recent years, with the Gini coefficient for disposable income rising to 26.8, up from 24.3 in 2009/10.
The median income of retired households was largely unaffected by the economic downturn and rose by 7.7% (£1,500) between 2007/08 and 2014/15. In contrast, non-retired households’ median income in 2014/15 remained 3.1% (£900) below its level in 2007/08.
Nôl i'r tabl cynnwys2. Trends in household incomes
In the financial year ending 2015 (2014/15), the median equivalised household disposable income in the UK was £25,700. After taking account of inflation1 and changes in household structures over time, this figure is comparable to the pre-economic downturn level observed in 2007/08 (£25,400).
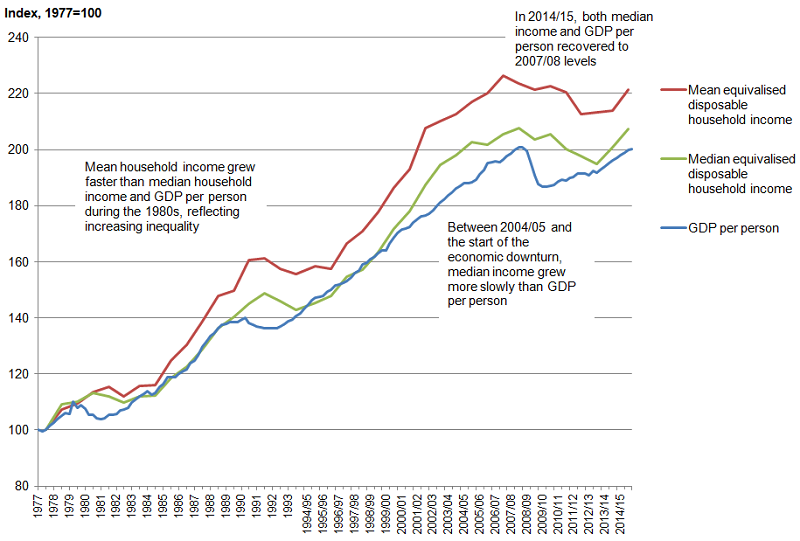
The impact of the economic downturn on median incomes was delayed relative to the fall in gross domestic product (GDP) per person (Figure 1). Between 2007/08 and 2009/10, GDP per person fell by 6.5%, while median disposable income changed little. Most of the decrease in median income occurred between 2009/10 and 2012/13 with median income in 2012/13 being £1,300 lower in real terms than in 2009/10. However, since 2012/13, there has been a real terms increase (of 6.4%) and by 2014/15, both median household income and GDP per person recovered to similar levels to those seen at the start of the economic downturn.
Mean equivalised disposable household income has also recovered to some extent, up to £30,900 in 2014/15, compared with £29,800 in 2012/13, though still below its 2006/07 peak of £31,600. Recent increases in average disposable incomes are due mainly to increases in income from employment. Average earnings grew in real terms in 2014/15 and continued growth in employment rates meant that this impact was felt more strongly in household incomes.
Preliminary estimates of key indicators such as median equivalised disposable income were released as Experimental Statistics in the bulletin “Nowcasting household income in the UK: financial year ending 2015” in October 2015. These preliminary estimates made use of “nowcasting” techniques in order to produce figures before full survey-based estimates are available. The preliminary estimates showed an increase of 3.2% in median income between 2013/14 and 2014/15, compared with a 3.3% increase in these final estimates, with the difference between the initial and final estimates less than £100 a year.
Figure 1: Growth of median (and mean) household income and gross domestic product (GDP) per person, 1977 to 2014/15
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this image Figure 1: Growth of median (and mean) household income and gross domestic product (GDP) per person, 1977 to 2014/15
.png (113.7 kB) .xls (54.3 kB)Taking a longer-term perspective (Figure 1), the median disposable income was over twice as high in 2014/15 as in 1977, growing from £12,400 at an average rate of 2.0% per year. Most of this increase in the value of median income occurred during the late 1980s and late 1990s.
Over this same period, mean household income increased at a marginally faster pace, growing at an average annual rate of 2.2% from £14,000 to £30,900. The faster growth of the mean measure was primarily due to incomes of high-income households growing at a faster rate between 1977 and 1990 than incomes in the middle and lower parts of the income distribution.
Growth in median household income closely mirrors growth in GDP per head for much of the time since 1977, rising during periods of economic growth and falling during or immediately after periods of negative growth . There has been a slight divergence between these two measures since the mid-1990s. Between 1995/96 and 2004/05, UK median household income grew at an average rate of 3.7% per year, faster than GDP per person, which grew at 2.6% per year. However, while GDP per person continued to grow at similar rates between 2004/05 and 2007/08, growth of median household income slowed to a fifth of its previous rate in the years immediately before the start of the economic downturn.
Growth in income across the distribution
The growth in incomes since 1977 has not been experienced evenly across the income distribution (Figure 2). The median disposable income for the richest fifth of households in 2014/15 was 2.4 times higher than in 1977, once inflation and household composition were accounted for. The median income of the poorest fifth of households has also grown over this time, but the rate of growth has been slower (1.9 times higher in 2014/15 than in 1977).
Figure 2: Growth in median equivalised household disposable income, 1977 to 2014/15 (2014/15 prices)
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 2: Growth in median equivalised household disposable income, 1977 to 2014/15 (2014/15 prices)
Image .csv .xls
Figure 3: Percentage change in median equivalised disposable income by quintile group between 2007/08 and 2014/15 (2014/15 prices)
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 3: Percentage change in median equivalised disposable income by quintile group between 2007/08 and 2014/15 (2014/15 prices)
Image .csv .xlsThe economic downturn had a negative impact on the incomes of all but the poorest fifth of the population. Between 2007/08 and 2012/13 (adjusting for household composition and inflation), average median disposable household income decreased for all but the poorest fifth of the population (Figure 3). The largest impact was on the middle and top fifths of the population where median incomes fell by £1,600 for the middle quintile and £4,400 for the top quintile (6.1% and 7.9% respectively in real terms), with similar falls in mean values. This has largely been driven by a fall in average income from employment (including self-employment) for these groups.
The real terms increase for the poorest fifth was mainly due to an increase in the average income from employment for this group, along with an increase in the average amount received in certain cash benefits such as tax credits and Jobseeker’s Allowance. The increase in average income from employment is associated with the changing make-up of this group since 2007/08. While the proportion of households in the bottom fifth whose “chief economic supporter” is either in employment or unemployed has increased, the proportion whose “chief economic supporter” is retired has fallen. This reflects an ongoing pattern of retired households moving up the overall income distribution, due to their incomes growing at a faster rate than those of non-retired households (see the incomes of retired households section for further details).
More recently, however, incomes have begun to recover. Between 2012/13 and 2014/15, average incomes increased across the income distribution, particularly towards the middle, reflecting increases in both wages and employment levels. The largest increase was for the middle fifth where median household income increased £1,500 in real terms (or 6.4%), reversing the fall following the economic crisis.
Notes for trends in household incomes
Estimates from previous years are adjusted for inflation using an implied deflator for the household sector and are equivalised using the modified OECD scale. For full details see Background Notes.
Throughout this release, 2014/15 represents the financial year ending 2015, April 2014 to March 2015 and similarly for earlier year spans.
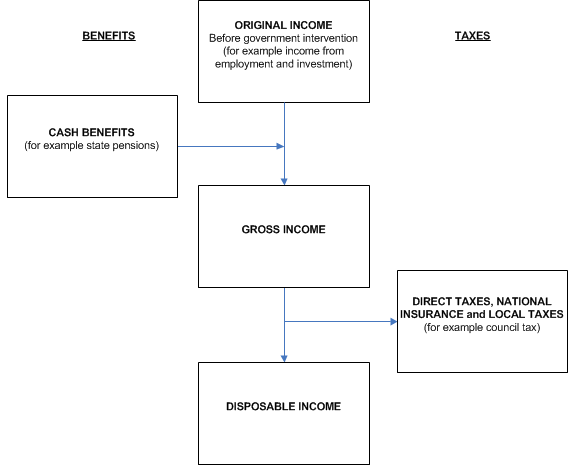
3. Redistribution of income through cash benefits and direct taxes
The overall impact of taxes and benefits are that they lead to income being shared more equally between households. This can be seen by comparing original income (income before any taxes and benefits have been taken into account) and gross income (income after the inclusion of cash benefits) with disposable income (income after inclusion of both cash benefits and direct taxes). In 2014/15, the richest fifth of households (those with an equivalised disposable income over £41,900) had an average original income of £83,800 per year, compared with £6,100 for the poorest fifth (those with an equivalised disposable income below £16,400) – a ratio of 14 to 1 (Figure 4). This ratio is broadly unchanged on 2013/14, indicating that inequality of original income has not changed substantially in the last year, according to this measure.
Figure 4: Original, gross and disposable income by quintile groups ALL households, 2014/15
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 4: Original, gross and disposable income by quintile groups ALL households, 2014/15
Image .csv .xlsImpact of cash benefits
In contrast to original income, the amount received from cash benefits such as tax credits, Housing Benefit and Income Support tends to be higher for poorer households than for richer households. In 2014/15, the highest amount of cash benefits was received by households in the second quintile group, £8,900 per year compared with £7,700 for households in the bottom group (Figure 5). This is largely because more retired households are located in the second quintile group compared with the bottom group and in this analysis the state pension is classified as a cash benefit.
Figure 5: Summary of the effects of direct taxes and cash benefits on ALL households, 2014/15
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 5: Summary of the effects of direct taxes and cash benefits on ALL households, 2014/15
Image .csv .xlsThe distribution of cash benefits between richer and poorer households has the effect of reducing inequality of income. After cash benefits are taken into account, the richest fifth had an average gross income that was roughly six times that of the poorest fifth (gross incomes of £86,800 per year compared with £13,800, respectively), a proportion broadly unchanged on 2013/14.
Looking at individual cash benefits, in 2014/15, the average combined amount of contribution-based and income-based Jobseeker’s Allowance (JSA) received by the bottom two quintile groups decreased compared with 2013/14 (Reference Table 2). This is largely due to fewer households receiving this benefit, consistent with a fall in unemployment between these years, as well as the ongoing implementation of the Universal Credit (UC) system which by April 2015 had been rolled out to 85,000 claimants1.
Claimants of UC and JSA are subject to the Claimant Commitment which outlines specific actions that the recipient must carry out in order to receive benefits. This may also have impacted on the number of households in receipt of these benefits. JSA rates, along with other working age benefits, were increased by 1% in 2014/15, below the CPI rate of inflation.
The phasing out of Incapacity Benefit, Severe Disablement Allowance and Income Support paid because of illness or disability and transfer of recipients to Employment and Support Allowance (ESA) has seen average amounts received from the former benefits fall in 2014/15, whilst average amounts received from ESA have risen, reflecting the increased number of claimants. The roll-out of Personal Independence Payment (PIP), which is replacing Disability Living Allowance (DLA) for adults aged under 652, also continued in 2014/15.
There was a 20.3% decrease in the amount of Child Benefit received by the richest fifth of households, due to fewer households in this part of the income distribution receiving this benefit. This is likely to be related to the High Income Benefit Charge, which came into effect in January 2013. From this date, those on higher incomes were liable to pay a charge equivalent to some or all of their child benefit entitlement. This is likely to have resulted in some households electing to stop getting Child Benefit (“opt out”) rather than pay the charge.
Impact of direct taxes
Direct taxes (Income Tax, employees’ National Insurance contributions, and Council Tax/Northern Ireland rates) also act to reduce inequality of income. Richer households pay both higher amounts of direct tax and a higher proportion of their income in direct taxes.
In 2014/15, on average, households paid £7,700 per year in direct taxes, equivalent to 18.8% of their gross income. The richest fifth of households paid on average £19,800 per year, the vast majority of which was Income Tax. This corresponds to 22.8% of their gross income, broadly unchanged on previous years. By contrast, the average direct tax bill for the poorest fifth, at £1,500 per year, was equivalent to 11.0% of gross household income for this group, also largely unchanged from last year. The largest component of direct taxes for the bottom quintile was Council Tax/Northern Ireland rates.
The poorest fifth of households had the largest annual percentage increase in the average amount paid in Income Tax in 2014/15, although the average amount paid as a proportion of their gross income was largely unchanged. This reflects both an increase in employment and an increase in the average amount received in wages and salaries in this part of the distribution, which has masked the effect of the increase in the personal allowance (from £9,440 in 2013/14 to £10,000 in 2014/15).
After direct taxes the richest fifth of households had average incomes that were around five and a half times that of the poorest fifth (£67,000 and £12,300 per year respectively), a ratio broadly similar to 2013/14.
Indirect taxes and benefits in kind
Indirect taxes on expenditure (such as VAT and fuel and alcohol duties) and benefits in-kind provided by the state (such as education services and the NHS) also play a significant role in the redistribution of income.
The full Effects of taxes and benefits on household income 2014/15 statistical bulletin, to be released in May 2016, will provide further analysis of household income including the impact of both of these.
Notes for redistribution of income through cash benefits and direct taxes
The number of people in the survey sample indicating they received Universal Credit (UC) was too small to allow it to be represented separately in this analysis. UC has therefore been classified under ‘other cash benefits’.
In England, Wales and Scotland.
Throughout this release, 2014/15 represents the financial year ending 2015, April 2014 to March 2015 and similarly for earlier year spans.
4. Longer-term trends in income inequality
There are a number of different ways in which inequality of household income can be presented and summarised. Perhaps the most widely used measure internationally is the Gini coefficient. Gini coefficients can vary between 0 and 100 and the lower the value, the more equally household income is distributed.
Analysis of Gini coefficients for all households over time (Figure 6) shows that the 1980s were characterised by a large increase in inequality of disposable income, particularly during the second half of that decade. Since then the changes have been smaller in scale. Inequality of disposable income reduced slowly from 1990 until the mid-1990s, but did not fully reverse the rise seen in the previous decade. In the late 1990s, income inequality rose slightly before falling once again in the early 2000s.
There has been a very gradual decline in inequality of disposable income on this measure since 2006/07. The Gini coefficient for disposable income in 2014/15 was 32.6%, effectively unchanged from its 2013/14 value of 32.4%.
There has been some variation over time in the extent to which cash benefits and direct taxes together work to decrease income inequality. This can be seen by comparing the Gini coefficients of original and gross income with the Ginis for disposable income (Figure 6). Cash benefits have the largest impact on reducing income inequality, with direct taxes acting to further reduce it.
Figure 6: Gini coefficients for original, gross and disposable income, 1977 to 2014/15
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 6: Gini coefficients for original, gross and disposable income, 1977 to 2014/15
Image .csv .xlsLooking at this relationship over time (Figure 6), in 1977, the combination of cash benefits and direct taxes had the effect of decreasing the Gini by 36.8%. This impact increased during the early 1980s and by 1984 cash benefits and direct taxes together decreased the Gini coefficient by 41.6%. This increase in their impact meant that the rise in inequality of disposable income was not as large as that for original income over this period. However, during the late 1980s, their redistributive impact weakened, and by 1990, they reduced the Gini by only 28.4%, accelerating the growth in inequality of disposable income. Most recently, there has been a slight increase in the effect of cash benefits and direct taxes on income inequality, with their impact on reducing the Gini rising from 32.6% in 2006/07 to 34.8% in 2014/15 (Reference Table 11).
The characteristics of the Gini coefficient make it particularly useful for making comparisons over time, between countries and before or after taxes and benefits. However, no indicator is completely without limitations and one drawback of the Gini is that, as a single summary indicator, it cannot distinguish between different-shaped income distributions. For that reason, it is useful to look at this index alongside other measures of inequality. One such measure is the quintile share ratio or the S80/S20 ratio. This is the ratio of the total equivalised disposable income of the richest fifth of the population to that of the poorest fifth of the population. The higher the ratio, the higher the level of income inequality. The pattern of change in this measure (Figure 7) is broadly the same as that seen with the Gini coefficient, with the most recent peak in inequality in 2007/08, which has been followed by a gradual decrease in levels of inequality.
Figure 7: S80/S20 ratio, 1977 to 2014/15
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 7: S80/S20 ratio, 1977 to 2014/15
Image .csv .xlsFurther analysis of changing income inequality over time will be published in April 2016 in "The effects of taxes and benefits on income inequality, 1977 to 2014/15”.
Notes for longer-term trends in income inequality
- Throughout this release, 2014/15 represents the financial year ending 2015, April 2014 to March 2015 and similarly for earlier year spans.
5. Incomes of retired and non-retired households
Figure 8 compares growth in the median disposable income of retired and non-retired households with that for all households, taking account of inflation and changes in household composition over time. For both groups of households, the value of the median disposable income has increased since 2012/13. However, the pattern of change since the start of the economic downturn has been very different for retired and non-retired households. While incomes of non-retired households remain higher than retired households, since 2007/08, the median income for retired households has increased in most years, with the value rising to £21,000 in 2014/15, £1,500 higher than in 2007/08. By contrast, the median income for non-retired households decreased, and was £2,600 lower in 2012/13 than in 2007/08. Since 2012/13, the value of the median for non-retired households has risen to £28,300, but is still around £900 below 2007/08 levels (£29,200).
Figure 8: Median equivalised disposable household income by household type (2014/15 prices)
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 8: Median equivalised disposable household income by household type (2014/15 prices)
Image .csv .xlsThese same patterns for retired and non-retired households are also observed in the value of mean disposable income. The growth in the incomes of retired households since 2007/08 has been driven by a number of factors. One is a rise in both the amounts received and the number of households reporting receipts from private pensions or annuities. Another is an increase in average income from the state pension, due in part to the impact of the "triple lock"1.
The fall in average disposable income for non-retired households after the economic downturn reflected largely a fall in income from employment (including self-employment). Similarly, it is earnings growth at the household level, in part due to rising employment levels, which has been the main driver of the most recent increases in average income for non-retired households.
While the income of retired households remains considerably lower than that of non-retired households, retired households have seen faster income growth over the period covered by this analysis. After adjusting for inflation, in 1977, the median income of retired households was £7,900 and the median income of non-retired households was £14,000. By 2014/15, the income of retired households had grown 2.7 times to £21,000, while the income of non-retired households had doubled from its 1977 level to £28,300.
Incomes of retired households
Retired households are those where the income of retired household members accounts for the majority of the total household gross income (see the background notes for the definition of a retired person). Retired households have different income patterns to their non-retired counterparts.
Retired households are much more likely to be towards the bottom of the overall income distribution than at the top of the distribution. Whereas retired households made up 34.4% and 39.4% of the bottom and second quintile groups respectively, they only made up 12.6% of the richest fifth of households in 2014/15. However, the relative position of retired households has improved over time. For example, 10 years previously (2004/05), retired households made up 45.7% of the bottom fifth and 6.1% of the top fifth of the income distribution (Figure 9).
Figure 9: Distribution of retired households in all-household population, 2004/05 and 2014/15
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 9: Distribution of retired households in all-household population, 2004/05 and 2014/15
Image .csv .xlsOn average, the poorest fifth of retired households received £8,100 per year from cash benefits in 2014/15 (Reference Table 6.) Those in the other quintile groups received, on average, between £11,100 and £12,700 per year. Cash benefits represented just under half (47.1%) of retired households’ total gross income on average, a proportion which was higher for poorer households and lower for richer households (74.5% for the poorest fifth of retired households and 25.3% for the richest fifth). Of the total value of retired households’ cash benefits, just over three-quarters (79.8%) was due to the State Pension, on average.
Figures 10a and 10b show how the sources of retired households’ gross incomes have changed over time. Overall, the proportion coming from cash benefits (including State Pension) has fallen significantly, from 64.7% in 1977 to the current level of 47.1%. This has mainly been due to growth in the percentage of retired households receiving income from private pensions and annuities, which rose from 44.5% in 1977 to 79.6% in 2014/15. In 1977, the average income received by retired households from private pensions was £1,600, accounting for 18% of the gross income of this group. By 2014/15, retired households received on average £10,300 from private pensions or annuities, equivalent to 43.0% of their gross income.
Figure 10a: Gross income of retired households by component, 1977 to 2014/15 (14/15 prices)
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 10a: Gross income of retired households by component, 1977 to 2014/15 (14/15 prices)
Image .csv .xls
Figure 10b: Percentage of gross income of retired households by component, 1977 to 2014/15
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 10b: Percentage of gross income of retired households by component, 1977 to 2014/15
Image .csv .xlsUntil 1999/2000, the State Pension was consistently the largest source of income for retired households. Since 2010/11, private pensions and annuities have consistently contributed most to gross income of retired households. After allowing for inflation, the State Pension doubled from an average of £4,700 in 1977 to £9,000 in 2014/15. The extent to which retired households are major beneficiaries from redistribution through direct taxes and cash benefits can be further seen by comparing average incomes of the top and bottom fifths of retired households. In 2014/15, before taxes and benefits, the richest fifth of retired households had an average total original income of £34,700 per year. This was over 12 times that of the poorest fifth (£2,800 per year). This ratio was reduced by cash benefits and direct taxes to just over 4 to 1.
Incomes of non-retired households
In 2014/15, the average original income for non-retired households was £42,800 per year. As might be expected, the original income of non-retired households showed a relatively strong relationship to the number of economically active people they contained. On average, households in each of the top three quintile groups contained almost twice as many economically active people as those in the poorest group.
Cash benefits provided 45.3% of gross income for non-retired households in the bottom fifth, falling to 1.8% for non-retired households in the richest fifth. Their payment results in a significant reduction in income inequality. The patterns for direct taxes are similar to those described for all households.
Figure 11: Percentage of gross income of non-retired households coming from cash benefits, 1977-2014/15
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 11: Percentage of gross income of non-retired households coming from cash benefits, 1977-2014/15
Image .csv .xlsFigure 11 shows how the proportion of non-retired households’ gross income coming from cash benefits has changed over time. In 1977, cash benefits accounted for 25.4% of the gross income of the poorest fifth of households. With the exception of a fall in the late 1980s, this proportion grew over the following 16 years, reaching a peak of 61.5% in 1993. Since then, the broad trend for this group has been downwards. The proportion of income coming from cash benefits for the second fifth also reached a peak in 1993, rising from 11.1% in 1977 to 23.1%, before falling again. However, unlike the poorest group, the proportion of income from cash benefits for the second fifth started to increase again after 2004/05, rising from 17.0% in that year to 24.5% in 2014/15.
Inequality among retired and non-retired households
Inequality of disposable income for both retired and non-retired households, measured using the Gini coefficient, has followed a similar trend to that for all households, increasing significantly during the 1980s (Figure 12). Since then the broad trend has been downwards, though income inequality levels remain above those seen in the late 1970s and early 1980s. There has been more year-on-year variation in the Gini coefficients for retired households than for the overall population, though this is primarily a consequence of the smaller sample size on which these estimates are based.
In recent years, there is evidence of a slight increase in inequality for retired households. In 2014/15, the Gini coefficient for disposable income amongst retired households was 26.8, up from 24.3 in 2009/10). In contrast, the Gini for non-retired households has fallen slightly over recent years, from 34.5 in 2006/07 to 33.2 in 2014/15.
Figure 12: Gini coefficients for disposable income by household type, 1977 to 2014/15
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 12: Gini coefficients for disposable income by household type, 1977 to 2014/15
Image .csv .xlsAnother way of looking at income inequality is to see what proportion of income is received by the richest fifth (20%) of households. Among retired households, there is a higher degree of income inequality before direct taxes and cash benefits than for non-retired households. In 2014/15, the richest fifth of retired households received 55.0% of total original income for all retired households (Table 6). In comparison, the richest fifth of non-retired households received 44.2% of total income for that group (Table 4).
Direct taxes and cash benefits also have a much greater impact on income inequality of retired households than non-retired households. After taking account of these, the share of income received by the richest fifth of households is reduced to 36.9%. As might be expected, given that the state pension is classified as a cash benefit in this analysis, the bulk of this reduction is due to the impact of cash benefits.
While direct taxes and cash benefits also reduce the share of income of the richest fifth of non-retired households, the reduction is much lower, reduced to 40.5% of disposable income. Again, the bulk of this reduction is caused by the impact of cash benefits.
Notes for incomes of retired and non-retired households
The triple lock is a government policy which guarantees to increase the basic state pension by the higher of CPI inflation, average earnings or a minimum of 2.5% every year.
Throughout this release, 2014/15 represents the financial year ending 2015, April 2014 to March 2015 and similarly for earlier year spans.
6. Economic context
In the financial year 2014/15, outcomes in the labour market are likely to have directly affected household incomes. In the three months to March 2015, both the number of people in employment (31.1 million) and the headline employment rate (73.5%) were at their highest levels since records began. The unemployment rate, which fell by 1.0 percentage point in the year to Quarter 1 (Jan to Mar) 2014, fell by a further 1.3 percentage points in the year to Quarter 1 (Jan to Mar) 2015 to reach 5.5%. The proportion of those aged over 16 who were inactive was broadly unchanged over this period. Taking these series together, this suggests that developing labour market conditions boosted household incomes over this period, by increasing the number of people in work.
Alongside this growth in employment, wages also began to show signs of recovery during this period. In the three months ending March 2015, annual wage growth was 2.3%, 1 percentage point higher than over the same period of 2014. Wage growth was stronger in finance and business services (3.2%) and in wholesale, retailing, hotels and restaurants (3.2%), and weaker in manufacturing (0.7%) over this period. Private sector pay growth, at 2.8%, was also stronger than in the public sector (excluding financial services), where pay grew by 1.3%. As a whole, the strengthening of average weekly earnings will have increased household incomes over this period.
Figure 13: Contributions to the growth of real regular pay: effect of Consumer Prices Index (CPI) inflation and the growth of average regular weekly earnings, 3-month on 3-months a year ago
UK
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this chart Figure 13: Contributions to the growth of real regular pay: effect of Consumer Prices Index (CPI) inflation and the growth of average regular weekly earnings, 3-month on 3-months a year ago
Image .csv .xlsStronger nominal wages have also raised the growth rate of real earnings as prices changed little on average between 2013/14 and 2014/15. Inflation, as measured by the Consumer Prices Index (CPI), was 0.0% in the year to March 2015, the lowest rate ever recorded and 1.6 percentage points lower than the previous year. Over the period between Quarter 2 (Apr to June) 2014 and Quarter 1 (Jan to Mar) 2015, the household final consumption expenditure measure of prices (the HHFCE implied deflator), which indicates the price changes that households faced when purchasing a broader range of products, grew by 0.2%, a fall of 1.1 percentage points compared with the same period in 2013/14 .
The low inflation experienced during this period, combined with the recovery in nominal wages, led to a resurgence in real wages and therefore purchasing power during the 2014/15 financial year. Annual regular pay growth in real terms (three month average) was negative between July 2008 and September 2014, became positive in October 2014 and increased to 2.2% in March 2015, its highest rate since November 2007.
In broader terms, the UK economy continued to grow in the financial year 2014/15, continuing the recovery which started in Quarter 3 (July to Sept) 2009. By the end of this period there had been nine quarters of consecutive increase in GDP. However, the growth rate of GDP eased from 2.2% in the financial year 2013/14, to 1.7% in 2014/15. By Quarter 1 (Jan to Mar) 2015, UK GDP was 5.0% above its pre downturn peak in Quarter 1 (Jan to Mar) 2008. GDP per head – which has recovered more slowly – was 0.3% below its pre-downturn peak by Quarter 1 (Jan to Mar) 2015.
Figure 14: Median equivalised household disposable income and Real Household Disposable Index (RHDI) per head, excluding NPISH, Q1 2008 to Q1 2015. Index Q1 2008=100
UK
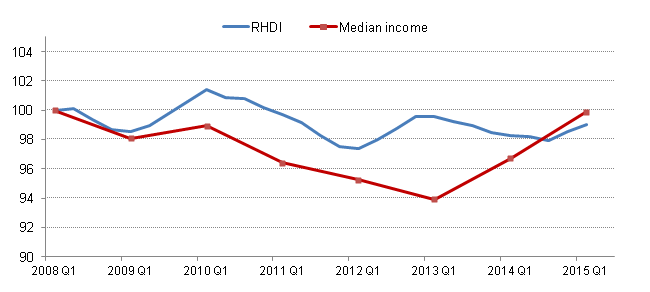
Source: Office for National Statistics
Download this image Figure 14: Median equivalised household disposable income and Real Household Disposable Index (RHDI) per head, excluding NPISH, Q1 2008 to Q1 2015. Index Q1 2008=100
.png (10.2 kB) .xls (28.2 kB)In early 2015, both median household disposable income and RHDI per head were at similar levels to those seen in early 2008. However, the paths of these measures have been notably different since early 2008. Median household disposable income fell 6.1% between the financial year 2007/08 and 2012/13 before recovering between 2012/13 and 2014/15. Figure 14 shows that changes in RHDI per head have been less pronounced; as RHDI has remained within 3% of its Quarter 1 (Jan to Mar) 2008 level during this period.
The deviation in the paths of the two measures in 2009 is likely to be due to the impact of lower interest rates during this period. While median household income includes gross interest receipts – which fell markedly during the downturn – RHDI includes a net measure of interest received which offset the fall in interest receipts with the reduction in interest paid by households. As a consequence, the net income measure in RHDI was more resilient over this period. Since 2013, however, median household income has grown more strongly than RHDI per head – likely reflecting the rising employment rate over this period, which in turn has increased median earnings per household. While RHDI has also been affected by the higher employment rate, it has a much larger impact on a median income measure, than on a measure of aggregate household income such as RHDI.
Notes for economic context
Throughout this release, 2014/15 represents the financial year ending 2015, April 2014 to March 2015 and similarly for earlier year spans.
Nôl i'r tabl cynnwys