1. Key points
In April 2012 median gross weekly earnings for full-time employees were £506, up 1.5% from £498 in 2011
For men, full-time earnings were £546, up 1.4%, compared with £449 for women, up 1.9%
The gender pay gap (i.e. the difference between men's and women's earnings as a percentage of men's earnings) based on median gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime) for full-time employees decreased to 9.6% from 10.5% in 2011
For the year ending 5 April 2012 median gross annual earnings for full-time employees (who had been in the same job for at least 12 months, including those whose pay was affected by absence) were £26,500, an increase of 1.4% from the previous year
Between 2011 and 2012 the gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime) for full-time employees in the bottom decile increased by 2.3% to £7.16 per hour. This compared with a fall of 0.2% in the top decile to £26.56 per hour
In April 2012 median gross weekly earnings for full-time employees were highest in London, at £653, and lowest in Wales, at £453
2. Summary
The Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) is based on a 1% sample of employee jobs. This is drawn from HM Revenue and Customs Pay As You Earn (PAYE) records. ASHE collects information on the levels, distribution and make-up of earnings and hours paid. Results are produced for various industrial, occupational and geographic breakdowns, as well as by public and private sectors and age groups.
This bulletin contains provisional estimates from the 2012 survey and revised estimates from the 2011 survey. Unless otherwise stated, all figures in this bulletin relate to employees on adult rates whose earnings for the survey pay period were not affected by absence.
Nôl i'r tabl cynnwys3. Weekly earnings
In April 2012 median gross weekly earnings for full-time employees were £506, up 1.5% from £498 in 2011.
Men’s median full-time weekly earnings increased by 1.4% to £546 between 2011 and 2012, compared with an increase of 1.9% for women to £449.
Figure 1: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by sex; UK, April 2011 and 2012
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional
Download this chart Figure 1: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by sex; UK, April 2011 and 2012
Image .csv .xlsPart-time median weekly earnings were £155 in April 2012, up 1.3% from 2011. For women, part-time weekly earnings were £158, compared with £146 for men.
The median gross weekly earnings for all employee jobs (full-time and part-time) were £405, an increase of 1.3% from 2011.
Figure 2: Median gross weekly earnings; UK, April 2011 and 2012
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional
Download this chart Figure 2: Median gross weekly earnings; UK, April 2011 and 2012
Image .csv .xls
Table 1: Median gross weekly earnings; UK, April 2011 and 2012
| £ per week | ||||
| Full-time | Part-time | All | ||
| April 2011 | Men | 538.2 | 142.5 | 493.0 |
| Women | 440.0 | 156.6 | 313.2 | |
| All | 498.3 | 153.0 | 400.0 | |
| April 2012 | Men | 545.8 | 145.8 | 497.6 |
| Women | 448.6 | 158.4 | 319.0 | |
| All | 505.9 | 155.0 | 405.0 | |
| Change % | Men | 1.4 | 2.3 | 0.9 |
| Women | 1.9 | 1.1 | 1.8 | |
| All | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.3 | |
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Figures rounded to one decimal place 4. 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional | ||||
Download this table Table 1: Median gross weekly earnings; UK, April 2011 and 2012
.xls (26.1 kB)4. Annual earnings
For the tax year ending 5 April 2012 the median gross annual earnings for full-time employees on adult rates who had been in the same job for at least 12 months (including those whose pay was affected by absence) were £26,500. This was an increase of 1.4% compared with £26,100 in the year ending 5 April 2011.
The median gross annual earnings for men were £28,700, up 1.2% from 2011, and for women were £23,100, up 2.0%.
Figure 3: Median full-time gross annual earnings by sex; UK, 2011 and 2012
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Employees on adult rates who have been in the same job for at least 12 months, including those whose pay was affected by absence
- Earnings for tax year ending 5 April
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional
Download this chart Figure 3: Median full-time gross annual earnings by sex; UK, 2011 and 2012
Image .csv .xls
Table 2: Median full-time gross annual earnings by sex; UK, 2011 and 2012
| £ thousands per year | |||
| Men | Women | All | |
| 2011 | 28.4 | 22.6 | 26.1 |
| 2012 | 28.7 | 23.1 | 26.5 |
| Change % | 1.2 | 2.0 | 1.4 |
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates who have been in the same job for at least 12 months, including those whose pay was affected by absence 2. Earnings for tax year ending 5 April 3. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 4. Figures rounded to one decimal place 5. 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional | |||
Download this table Table 2: Median full-time gross annual earnings by sex; UK, 2011 and 2012
.xls (25.6 kB)5. Hourly earnings (excluding overtime)
Excluding overtime, median gross hourly earnings of full-time employees were £12.76 per hour in April 2012, up 1.6% on 2011. The median hourly earnings of men increased by 1.1% compared with an increase of 2.2% for women.
Figure 4: Median gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2011 and 2012
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional
Download this chart Figure 4: Median gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2011 and 2012
Image .csv .xls
Table 3: Median gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2011 and 2012
| £ per hour | ||||
| Full-time | Part-time | All | ||
| April 2011 | Men | 13.12 | 7.64 | 12.41 |
| Women | 11.75 | 8.03 | 9.90 | |
| All | 12.56 | 7.99 | 11.07 | |
| April 2012 | Men | 13.27 | 7.72 | 12.50 |
| Women | 12.00 | 8.12 | 10.04 | |
| All | 12.76 | 8.01 | 11.21 | |
| Change % | Men | 1.1 | 1.0 | 0.7 |
| Women | 2.2 | 1.2 | 1.4 | |
| All | 1.6 | 0.2 | 1.2 | |
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Earnings rounded to two decimal places, percentages rounded to one decimal place 4. 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional | ||||
Download this table Table 3: Median gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2011 and 2012
.xls (26.6 kB)Gender pay differences
The earnings of women relative to men vary according to whether an employee works full-time or part-time. Median gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime) of part-time employees were 37.2% less than the earnings of full-time employees in April 2012. At the same time, the Labour Force Survey shows that the UK workforce consisted of approximately 12.7 million males (51% of the employee workforce) and 12.3 million females (49% of the workforce).
There is a difference in the proportion of male and female employees who worked full- and part-time. For male employees, 88% worked full-time and 12% worked part-time, while the comparable figures for female employees were 58% and 42% respectively. This highlights the fact that more women work part-time than men and consequently they are more likely to receive lower hourly rates of pay.
Figure 5: Employee workforce composition; UK, 2012 Q2
Source: Labour Force Survey - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Based on seasonally adjusted data
- Split between full-time and part-time employment based on respondents' self-classification
Download this chart Figure 5: Employee workforce composition; UK, 2012 Q2
Image .csv .xls
Table 4: Employee workforce composition; UK, 2012 Q2
| Employees, thousands | ||||||
| Men | % of total | Women | % of total | All | % of total | |
| Full-time | 11,178 | 87.7 | 7,131 | 58.1 | 18,308 | 73.2 |
| Part-time | 1,565 | 12.3 | 5,147 | 41.9 | 6,712 | 26.8 |
| All | 12,743 | 100.0 | 12,278 | 100.0 | 25,020 | 100.0 |
| Source: Labour Force Survey - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Number of employees to nearest thousand, seasonally adjusted 2. Split between full-time and part-time employment based on respondents' self-classification 3. Percentages rounded to one decimal place | ||||||
Download this table Table 4: Employee workforce composition; UK, 2012 Q2
.xls (26.1 kB)In April 2012 men’s median gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime) grew by 1.1% to £13.27, up from £13.12 in 2011. In comparison, women’s hourly earnings were £12.00, a 2.2% increase compared with £11.75 in 2011. The gender pay gap (i.e. the difference between men's and women's hourly earnings as a percentage of men's earnings) for full-time employees therefore decreased to 9.6% from 10.5% in 2011.
Part-time
For part-time employees, men’s median gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime) were £7.72 in April 2012, up 1.0% from £7.64 in 2011. In comparison, women’s hourly earnings were £8.12, an increase of 1.2% from £8.03. The gender pay difference for part-time employees was therefore in the opposite direction to that of full-time employees, widening slightly to -5.2%, compared with -5.1% in 2011.
All
In April 2012 the gender pay gap based on median hourly earnings for all employees (full-time and part-time) decreased to 19.7% from 20.2% in 2011.
Figure 6: Gender pay gap for median gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2000 to 2012
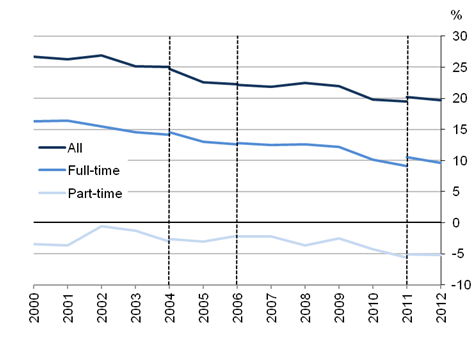
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Download this image Figure 6: Gender pay gap for median gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2000 to 2012
.png (35.4 kB)
Table 5: Median gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime) with gender pay differences; UK, April 2011 and 2012
| £ per hour | |||||
| Men | Women | Pay gap % | |||
| April 2011 | Full-time | 13.12 | 11.75 | 10.5 | |
| Part-time | 7.64 | 8.03 | -5.1 | ||
| All | 12.41 | 9.90 | 20.2 | ||
| April 2012 | Full-time | 13.27 | 12.00 | 9.6 | |
| Part-time | 7.72 | 8.12 | -5.2 | ||
| All | 12.50 | 10.04 | 19.7 | ||
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Percentages represent the difference between men's and women's hourly earnings as a percentage of men's earnings 4. Earnings rounded to two decimal places, percentages rounded to one decimal place 5. 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional | |||||
Download this table Table 5: Median gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime) with gender pay differences; UK, April 2011 and 2012
.xls (26.1 kB)Mean hourly earnings (excluding overtime)
Although ONS’s headline estimates of gender pay differences are based on median hourly earnings (excluding overtime), mean hourly earnings provide a useful supplementary measure.
Full-time
Men’s mean gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime) were £16.50 in April 2012, up 0.4% from £16.43 in 2011. Women’s mean hourly earnings increased by 1.7% to £14.05 compared with £13.82 in 2011. This means that the gender pay difference for full-time employees narrowed to 14.9% from 15.9% in 2011.
Part-time
For part-time employees, men’s mean hourly earnings (excluding overtime) were £11.71, down from £11.88 in 2011, compared with women’s hourly earnings of £10.79, up from £10.70. The gender pay gap for part-time employees has therefore narrowed to 7.9%, from 9.9% in 2011. This is in contrast to the pay gap for median earnings, which is in the opposite direction. The reason for this is that there are a larger number of men than women who are working part-time with high earnings, which skews the distribution and increases the mean relative to the median.
All
The gender pay difference based on the mean for all employees has decreased to 18.6% in 2012 from 19.6% in 2011.
Figure 7: Gender pay gap for mean gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2000 to 2012
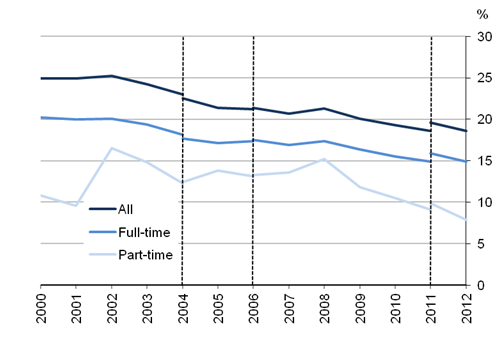
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- Dashed lines represent discontinuities in 2004, 2006 and 2011 ASHE estimates (see background notes)
- Gender pay gap defined as difference between men's and women's hourly earnings as a percentage of men's earnings
- 2012 data are provisional
Download this image Figure 7: Gender pay gap for mean gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2000 to 2012
.png (36.4 kB)
Table 6: Mean gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime) with gender pay differences; UK, April 2011 and 2012
| £ per hour | ||||
| Men | Women | Pay gap % | ||
| April 2011 | Full-time | 16.43 | 13.82 | 15.9 |
| Part-time | 11.88 | 10.70 | 9.9 | |
| All | 16.14 | 12.98 | 19.6 | |
| April 2012 | Full-time | 16.50 | 14.05 | 14.9 |
| Part-time | 11.71 | 10.79 | 7.9 | |
| All | 16.19 | 13.17 | 18.6 | |
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Percentages represent the difference between men's and women's hourly earnings as a percentage of men's earnings 4. Earnings rounded to two decimal places, percentages rounded to one decimal place 5. 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional | ||||
Download this table Table 6: Mean gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime) with gender pay differences; UK, April 2011 and 2012
.xls (26.1 kB)Distribution of hourly earnings (excluding overtime)
Between 2011 and 2012 the hourly earnings (excluding overtime) for full-time employees in the bottom decile grew by 2.3%, compared with a decrease of 0.2% for the top decile. The comparable figures for part-time employees were an increase of 2.5% and a decrease of 1.1% respectively.
In 2012 10% of full-time employees earned less than £7.16 per hour, while 10% earned more than £26.56 per hour.
The hourly earnings for the top decile of full-time employees were 208% of the median while the hourly earnings of the bottom decile were 56% of the median.
Figure 8: Distribution of gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2012
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- 2012 data are provisional
Download this chart Figure 8: Distribution of gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2012
Image .csv .xls
Table 7: Distribution of gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2012
| £ per hour | ||||
| Full-time | Part-time | All | ||
| Men | 10% earned less than | 7.38 | 6.08 | 6.75 |
| 50% earned less than | 13.27 | 7.72 | 12.50 | |
| 10% earned more than | 28.85 | 22.83 | 28.23 | |
| Women | 10% earned less than | 6.92 | 6.08 | 6.25 |
| 50% earned less than | 12.00 | 8.12 | 10.04 | |
| 10% earned more than | 23.37 | 18.81 | 21.75 | |
| All | 10% earned less than | 7.16 | 6.08 | 6.44 |
| 50% earned less than | 12.76 | 8.01 | 11.21 | |
| 10% earned more than | 26.56 | 19.71 | 24.95 | |
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Figures rounded to two decimal places 4. 2012 data are provisional | ||||
Download this table Table 7: Distribution of gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2012
.xls (26.1 kB)Gender pay differences
In April 2012 the gender pay gap for full-time employees in the top decile, at 19.0%, was larger than those for the median and bottom decile.
For part-time employees, there was no gender pay gap for the bottom decile, a gap of -5.2% for the median (i.e. women’s earnings were higher than men’s), and a gap of 17.6% for the top decile.
For all employees (full-time and part-time), the gender pay difference was smallest in the bottom decile, at 7.3%, and largest in the top decile, at 22.9%.
Table 8: Gender pay difference by distribution of gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2012
| % | ||||||||
| Full-time | Part-time | All | ||||||
| Bottom decile | 6.2 | 0.0 | 7.3 | |||||
| Median | 9.6 | -5.2 | 19.7 | |||||
| Top decile | 19.0 | 17.6 | 22.9 | |||||
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Figures represent the difference between men's and women's hourly earnings as a percentage of men's earnings 4. Figures rounded to one decimal place 5. 2012 data are provisional | ||||||||
Download this table Table 8: Gender pay difference by distribution of gross hourly earnings (excluding overtime); UK, April 2012
.xls (25.6 kB)6. Public and private sector pay
The median gross weekly pay of full-time employees in the public sector was £565 in 2012, up 1.6% from £556 in 2011. For the private sector the comparable figure was £479, up 1.5% from £472 in 2011.
The compositions of the public and private sectors are different. Consequently differences in gross weekly earnings do not reveal differences in rates of pay for comparable jobs. For example, many of the lowest paid occupations, such as bar and restaurant staff, hairdressers, elementary sales occupations and cashiers, exist primarily in the private sector, while there are a larger proportion of graduate-level and professional occupations in the public sector.
Figure 9: Median full-time gross weekly earnings for public and private sectors; UK, April 2011 and 2012
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- Private sector comprised of businesses whose legal status is defined as “Company”, “Sole Proprietor” or “Partnership”; public sector comprised of those defined as “Public Corporation”, “Central Government” or “Local Authority”
- 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional
Download this chart Figure 9: Median full-time gross weekly earnings for public and private sectors; UK, April 2011 and 2012
Image .csv .xls
Table 9: Median full-time gross weekly earnings for public and private sectors; UK, April 2011 and 2012
| £ per week | |||
| Public sector | Private sector | ||
| April 2011 | 555.6 | 471.9 | |
| April 2012 | 564.6 | 479.1 | |
| Change % | 1.6 | 1.5 | |
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Private sector comprised of businesses whose legal status is defined as “Company”, “Sole Proprietor” or “Partnership”; public sector comprised of those defined as “Public Corporation”, “Central Government” or “Local Authority” 4. Figures rounded to one decimal place 5. 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional | |||
Download this table Table 9: Median full-time gross weekly earnings for public and private sectors; UK, April 2011 and 2012
.xls (26.1 kB)7. Earnings by age group
In April 2012 the distribution of median gross weekly earnings for full-time employees showed that earnings were highest for the 40 to 49-year-old age group, at £573. Median gross weekly earnings increased until employees reached this age band and steadily decreased thereafter.
Figure 10: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by age group; UK, April 2012
Age
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- All employees aged 16-17 and employees on adult rates whose pay was unaffected by absence
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- 2012 data are provisional
Download this chart Figure 10: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by age group; UK, April 2012
Image .csv .xlsThere were some differences between the distribution of earnings by age for men and women. Men’s median weekly earnings were highest in the 40 to 49-year-old age group, at £622, whereas women’s earnings were highest in the 30 to 39-year-old age group, at £527.
Table 10: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by age group; UK, April 2012
| £ per week | ||||||
| Age group | Men | % change from 2011 | Women | % change from 2011 | All | % change from 2011 |
| 16-17 | 166.7 | -0.5 | 121.1 | -18.9 | 161.4 | -0.5 |
| 18-21 | 295.9 | 3.8 | 266.1 | 2.5 | 279.6 | 2.1 |
| 22-29 | 420.2 | 1.6 | 402.5 | 2.3 | 412.0 | 2.0 |
| 30-39 | 574.9 | 0.0 | 526.8 | 2.5 | 557.2 | 1.2 |
| 40-49 | 622.3 | 0.9 | 484.5 | 3.3 | 572.6 | 2.2 |
| 50-59 | 598.4 | 1.5 | 446.1 | 0.6 | 536.1 | 1.0 |
| 60+ | 509.2 | 2.1 | 407.4 | 2.9 | 477.8 | 2.4 |
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. All employees aged 16-17 and employees on adult rates whose pay was unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Figures rounded to one decimal place 4. 2012 data are provisional | ||||||
Download this table Table 10: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by age group; UK, April 2012
.xls (26.6 kB)8. Regional earnings
In April 2012 median gross weekly earnings for full-time employees were highest in London, at £653 (29% higher than the national median), and lowest in Wales, at £453 (11% lower than the national median).
Figure 11: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by region; UK, April 2012
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- 2012 data are provisional
Download this chart Figure 11: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by region; UK, April 2012
Image .csv .xlsThe regional earnings distribution differed by sex. While weekly earnings were highest in London for both sexes, earnings for men were lowest in Northern Ireland, at £479, and for women they were lowest in the East Midlands, at £402.
Table 11: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by region; UK, April 2012
| £ per week | ||||||
| Region | Men | % change from 2011 | Women | % change from 2011 | All | % change from 2011 |
| United Kingdom | 545.8 | 1.4 | 448.6 | 1.9 | 505.9 | 1.5 |
| North East | 490.3 | 0.7 | 407.0 | -0.5 | 455.1 | 1.3 |
| North West | 505.8 | 1.4 | 420.3 | 1.9 | 469.9 | 2.3 |
| Yorkshire and The Humber | 501.7 | 0.7 | 412.0 | 2.3 | 464.7 | 0.9 |
| East Midlands | 508.3 | 2.1 | 402.5 | 2.1 | 464.4 | 1.3 |
| West Midlands | 508.1 | 1.3 | 409.0 | 1.7 | 469.2 | 1.0 |
| East | 538.7 | 1.1 | 425.9 | 1.0 | 495.2 | 1.2 |
| London | 707.4 | 0.1 | 591.6 | 1.9 | 652.8 | 0.7 |
| South East | 588.6 | 0.9 | 461.8 | 2.3 | 536.6 | 1.4 |
| South West | 506.8 | -0.3 | 411.8 | 2.3 | 467.0 | 1.2 |
| Wales | 482.4 | 0.0 | 403.9 | 1.4 | 452.6 | 0.3 |
| Scotland | 533.1 | 3.0 | 438.1 | 0.6 | 497.6 | 2.6 |
| Northern Ireland | 478.9 | 3.7 | 440.0 | 5.3 | 459.5 | 3.3 |
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Figures rounded to one decimal place 4. 2012 data are provisional | ||||||
Download this table Table 11: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by region; UK, April 2012
.xls (26.6 kB)9. Earnings by occupation
In April 2012 median gross weekly earnings for full-time employees were highest for Managers and Senior Officials, at £738 (46% higher than the median for all employees), and lowest for Sales and Customer Service occupations, at £323 (36% lower than the median for all employees).
Table 12: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by major occupation group; UK, April 2012
| £ per week | |||
| Major occupation group | Men | Women | All |
| All | 545.8 | 448.6 | 505.9 |
| 1 - Managers, directors and senior officials | 797.9 | 625.4 | 738.4 |
| 2 - Professional occupations | 739.8 | 653.3 | 694.3 |
| 3 - Associate professional and technical occupations | 617.5 | 516.5 | 575.0 |
| 4 - Administrative and secretarial occupations | 431.0 | 381.5 | 393.1 |
| 5 - Skilled trades occupations | 476.6 | 346.4 | 465.7 |
| 6 - Caring, leisure and other service occupations | 371.5 | 322.5 | 332.7 |
| 7 - Sales and customer service occupations | 338.0 | 309.1 | 323.3 |
| 8 - Process, plant and machine operatives | 441.3 | 310.9 | 426.4 |
| 9 - Elementary occupations | 354.0 | 279.0 | 333.0 |
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Occupations as defined by the Standard Occupational Classification 2010 4. Figures rounded to one decimal place 5. 2012 data are provisional | |||
Download this table Table 12: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by major occupation group; UK, April 2012
.xls (26.1 kB)Again, there were some differences in the distribution of earnings for men and women. The highest and lowest earnings by major occupation group for men mirrored that of the overall distribution. However, for women, weekly earnings were highest in Professional occupations, at £653, and lowest in Elementary occupations, at £279.
Figure 12: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by major occupation group; UK, April 2012
Major occupation group
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- Occupations as defined by the Standard Occupational Classification 2010
- 2012 data are provisional
Download this chart Figure 12: Median full-time gross weekly earnings by major occupation group; UK, April 2012
Image .csv .xls10. The make-up of earnings
Additional payments (i.e. overtime, bonuses, commission and shift pay) accounted for 5.1% of mean full-time gross weekly earnings in April 2012. For male employees additional earnings accounted for 6.1% of mean total weekly earnings compared with 3.1% for women.
Figure 13: Components of full-time mean gross weekly earnings; UK, April 2012
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- Calculation of mean includes zero responses
- 2012 data are provisional
Download this chart Figure 13: Components of full-time mean gross weekly earnings; UK, April 2012
Image .csv .xls
Table 13: Components of full-time mean gross weekly earnings; UK, April 2012
| £ per week | |||||
| Gross pay | Overtime | Bonuses or commission | Shift, etc. | Component subtotal | |
| Men | 660.1 | 22.7 | 10.6 | 6.9 | 40.2 |
| Women | 524.4 | 6.8 | 3.9 | 5.5 | 16.1 |
| All | 607.1 | 16.5 | 7.9 | 6.4 | 30.8 |
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Calculation of mean includes zero responses 4. Figures rounded to one decimal place 5. 2012 data are provisional | |||||
Download this table Table 13: Components of full-time mean gross weekly earnings; UK, April 2012
.xls (25.6 kB)11. Total weekly and overtime paid hours
In April 2012 full-time employees worked a mean average of 39.1 paid hours per week (including overtime). In comparison, part-time employees worked 18.1 hours per week.
For full-timers, men’s weekly paid hours have decreased by 0.1 hours since April 2011 and women’s paid hours have remained the same. For part-time men there was a 0.1 hour increase in mean weekly paid hours and for women, again, there was no change.
Figure 14: Mean full-time weekly paid hours of work; UK, April 2011 and 2012
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional
Download this chart Figure 14: Mean full-time weekly paid hours of work; UK, April 2011 and 2012
Image .csv .xls
Table 14: Mean weekly paid hours of work; UK, April 2011 and 2012
| Hours per week | ||||
| Full-time | Part-time | All | ||
| April 2011 | Men | 40.2 | 17.6 | 37.1 |
| Women | 37.4 | 18.3 | 29.0 | |
| All | 39.1 | 18.1 | 33.1 | |
| April 2012 | Men | 40.1 | 17.7 | 37.0 |
| Women | 37.4 | 18.3 | 29.1 | |
| All | 39.1 | 18.1 | 33.1 | |
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Figures rounded to one decimal place 4. 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional | ||||
Download this table Table 14: Mean weekly paid hours of work; UK, April 2011 and 2012
.xls (25.6 kB)The proportion of full-time employees working paid overtime in April 2012 was 18.6%, up 0.2 percentage points from 2011. Full-time employees worked a mean average of 1.1 paid overtime hours per week in 2012. The percentage of full-time men who worked paid overtime has risen from 22.7% to 22.9% between 2011 and 2012. There has also been an increase for full-time women over the same period, from 11.7% to 12.0%.
Figure 15: Full-time mean weekly paid overtime hours; UK, April 2011 and 2012
Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE) - Office for National Statistics
Notes:
- Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence
- Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions)
- 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional
Download this chart Figure 15: Full-time mean weekly paid overtime hours; UK, April 2011 and 2012
Image .csv .xls
Table 15: Mean weekly paid overtime hours worked; UK, April 2011 and 2012
| Hours per week | |||||
| Full-time | % who worked overtime | Part-time | % who worked overtime | ||
| April 2011 | Men | 1.5 | 22.7 | 1.1 | 15.4 |
| Women | 0.5 | 11.7 | 0.7 | 15.9 | |
| All | 1.1 | 18.4 | 0.8 | 15.7 | |
| April 2012 | Men | 1.5 | 22.9 | 1.2 | 16.0 |
| Women | 0.5 | 12.0 | 0.7 | 15.7 | |
| All | 1.1 | 18.6 | 0.8 | 15.7 | |
| Source: Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings - Office for National Statistics Notes: 1. Employees on adult rates, pay unaffected by absence 2. Full-time defined as employees working more than 30 paid hours per week (or 25 or more for the teaching professions) 3. Figures rounded to one decimal place 4. 2011 data are revised, 2012 data are provisional | |||||

